According to new report By EIA, Uranium concentrate production in the United States was nearly 10 times higher than the previous year in 2022, partly as a result of higher prices . The is used in U.S. nuclear power reactors is largely imported because it’s more abundant and cheaper to produce in other countries. Uranium is used to power commercial nuclear reactors that produce electricity and to produce isotopes used for medical, industrial, and military equipments and other industrial purposes .
According to Worlds Nuclear power association, Nuclear energy now provides about 10% of the world’s electricity from about 440 power reactors. Nuclear is the world’s second largest source of low-carbon power (26% of the total in 2020). Over 50 countries utilize nuclear energy in about 220 research reactors. In addition to research, these reactors are used for the production of medical and industrial isotopes, as well as for training.
The U.S. Department of Energy is planning to reduce reliance on uranium imports. In 2020, Congress established a strategic uranium reserve, a stockpile of domestically produced uranium that serves as backup supply for U.S. nuclear power plants and incentivizes domestic uranium production. At the end of 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy awarded the first U3O8 supply contracts for the reserve, including one to White Mesa’s operator, Energy Fuels.
Global demand for electricity is set to grow near 100 percent by 2050. As the only energy source of low-carbon, scalable, reliable, and affordable electricity, nuclear is set to play a prominent role in meeting this growing demand while satisfying decarbonization objectives globally.
Albanian Minerals CEO Sahit Muja said, ” Uranium is indispensable metal, a essential components in clean energy production . Demand for uranium minerals will grow quickly as clean energy transitions gather pace. The world need to promote responsible and sustainable development of mineral resources, and offers vital insights for policy makers to build a new comprehensive global approach to uranium safety production and supply security”.
Here is the list of largest uranium producing countries in the world, according to World Nuclear Association.
Kazakhstan: Kazakhstan is currently the leading producer of uranium in the world. As mentioned above, the country’s total uranium output of 24,575 tons accounted for 39% of global uranium supply in 2016. Kazakhstan was home to 745,300 tons (13%) of known recoverable uranium resources as of 2015, second only to Australia. Kazatomprom, the country’s state-owned atomic company set up in 1997, controls all uranium exploration, mining as well as other nuclear-related activities. Many of the company’s mining operations are run as joint ventures with Russian, Chinese, Canadian and French counterparts.
Canada: Canada’s share of known world uranium resources was about 9% (509,000 tons) as of 2015, but it accounted for 22% of global output in 2016, making it the second largest producer in the world behind Kazakhstan. Last year, the country produced 14,039 tons of uranium. The world’s two top uranium mines – Cigar Lake and McArthur River – are located in Northern Saskatchewan, and Cameco owns majority stake in both of them. Canada uses only one fifth for domestic purposes and exports majority of uranium it produces.
Australia: Australia’s uranium production increased from 5,654 tons in 2015 to 6,315 tons in 2016, accounting for 10% of global output. It held 29% (1,664,100 tons) of the world’s known recoverable uranium resources as of 2015. While Australia holds the largest uranium resource of any country, mining bans and restrictions in various states leave a number of uranium mining projects in limbo.
Today, the nuclear industry is characterized by international commerce. A reactor under construction in Asia today may have components supplied from South Korea, Canada, Japan, France, Germany, Russia, and other countries. Similarly, uranium from Australia or Namibia may end up in a reactor in the UAE, having been converted in France, enriched in the Netherlands, deconverted in the UK and fabricated in South Korea.
The uses of nuclear technology extend well beyond the provision of low-carbon energy. It helps control the spread of disease, assists doctors in their diagnosis and treatment of patients, and powers our most ambitious missions to explore space. These varied uses position nuclear technologies at the heart of the world’s efforts to achieve sustainable development. For more information, see page on Nuclear Energy and Sustainable Development.
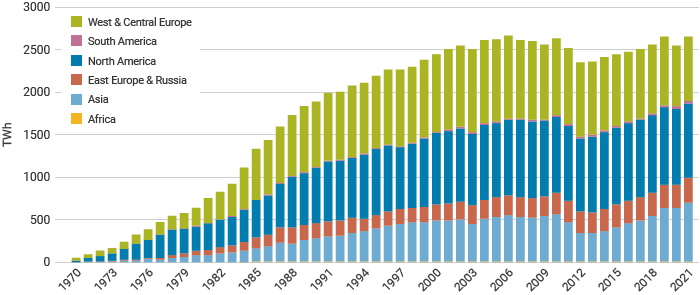
In 2021 nuclear plants supplied 2653 TWh of electricity, up from 2553 TWh in 2020.
Discover more from Green Innovation News
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




